

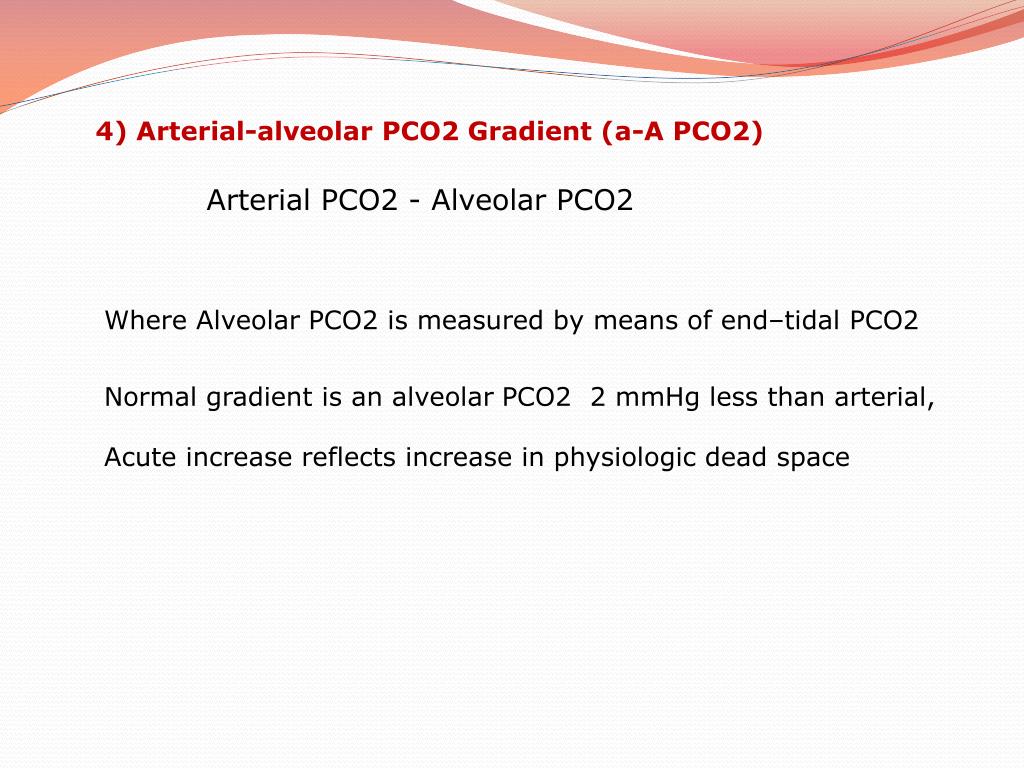
pointed out that increasing positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) in ARDS augments blood oxygenation and decreases shunt. However, if data generated breath-by-breath by capnographs are not integrated and analyzed together with data coming from other physiologic monitors and lung image analysis, their clinical meaning could be incomplete and even misleading. Modern volumetric capnographs incorporate this physiologic approach, enabling intensivists to measure VD/VTphys at the bedside. Currently, dead space is measured at the bedside by volumetric capnography, which reports expired CO 2 elimination as a function of expired VT, and VD/VTphys is calculated using the Enghoff’s modification of Bohr’s original equation: VD/VTphys = (PaCO 2 – PECO 2)/PaCO 2, where PaCO 2 is the arterial partial pressure of CO 2 obtained by arterial blood sampling and PECO 2 is an estimate of mixed expired partial pressure of CO 2 obtained from the mid-portion of phase III of the volumetric capnogram. The physiologic ventilatory dead space fraction (VD/VTphys) is usually defined as the fraction of tidal volume (VT) that does not participate in gas exchange.
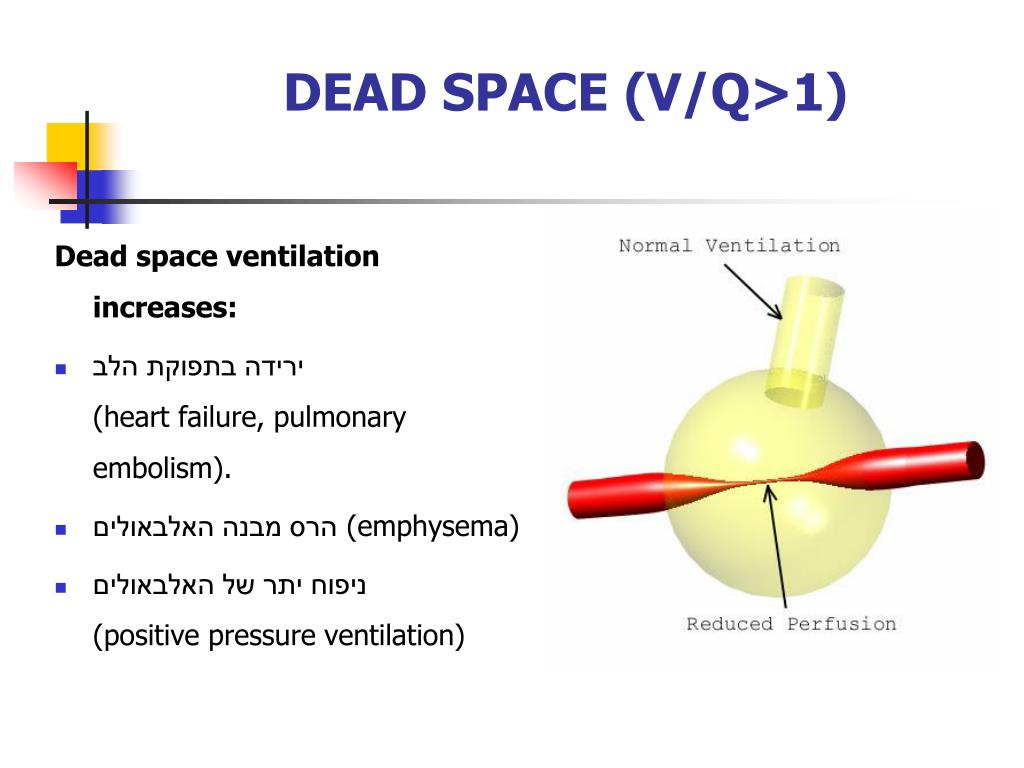
Dead space comprises two separate components: airway dead space (the volume of areas that do not contribute to gas exchange) and alveolar dead space (the volume of well-ventilated alveoli that receive minimal blood flow). Dead space refers to lung areas that are ventilated but not perfused.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
